Grade 8 - Claim 1 - Target J
 Back to Results
Back to ResultsClaim 1
Concepts and Procedures
Standards
SP-1
Construct and interpret scatter plots for bivariate measurement data to investigate patterns of association between two quantities. Describe patterns such as clustering, outliers, positive or negative association, linear association, and nonlinear association....
SP-2
Know that straight lines are widely used to model relationships between two quantitative variables. For scatter plots that suggest a linear association, informally fit a straight line, and informally assess the model...
SP-3
Use the equation of a linear model to solve problems in the context of bivariate measurement data, interpreting the slope and intercept. For example, in a linear model for a biology experiment, interpret...
SP-4
Understand that patterns of association can also be seen in bivariate categorical data by displaying frequencies and relative frequencies in a two-way table. Construct and interpret a two-way table summarizing data on...
Clarifications
Tasks for this target will often be paired with 8.F Target F and ask students to determine the rate of change and initial value of a line suggested by examining bivariate data. Interpretations related...
Range Achievement Level Descriptors
Evidence Required
1
The student interprets patterns of association between two quantities in a scatter plot (clustering in reference to the line of best fit, positive or negative association, linear association, nonlinear association, and the...
2
The student identifies the slope (rate of change) and intercept (initial value) of a line suggested by examining bivariate measurement data in a scatter plot.
3
The student constructs and interprets a two-way table summarizing data on two categorical variables collected from the same subjects.
4
The student uses relative frequencies calculated for rows or columns to describe possible association between the two variables.
Item Guidelines

Depth of Knowledge
M-DOK1
Recall includes the recall of information such as fact, definition, term, or a simple procedure, as well as performing a simple algorithm or applying a formula. That is, in mathematics a one-step, well-defined, and straight algorithmic procedure should be...
M-DOK2
Skill/Concept includes the engagement of some mental processing beyond a habitual response. A Level 2 assessment item requires students to make some decisions as to how to approach the problem or activity, whereas Level 1 requires students to demonstrate a...
Allowable Item Types
- Matching Tables
- Multiple Choice, single correct response
Allowable Stimulus Materials
Scatter plot, two-way relative frequency table, raw data
Key/Construct Relevant Vocabulary
cluster, data, frequency, initial value, line of best fit, trend line, linear extrapolation, linear association, negative association, outlier, positive association, rate of change, relative frequency, scale, scatter plot, slope, two-way relative frequency table, variable,...
Allowable Tools
Calculator
Target-Specific Attributes
None
Accessibility
Item writers should consider the following Language and Visual Element/Design guidelines [1] when developing items. Language Key Considerations: Use simple, clear, and easy-to-understand language needed to assess the construct or aid in the understanding of the...
Development Notes
Assessing the fit of a model (8.SP.A.2) will be assessed in Claim 4. Interpreting the slope and y-intercept in context (8.SP.A.3) will be assessed in Claims 2 and 4.


Task Models
Task Model 1a

Item Types
Matching TablesDepth of Knowledge
M-DOK1Standards
SP-1
Target Evidence Statement
The student interprets patterns of association between two quantities in a scatter plot (clustering in reference to the line of best fit, positive or negative association, linear association, nonlinear association, and the effect of outliers) and interprets the slope and...
Allowable Tools
Calculator
Task Description
Prompt Features: The student is prompted to determine whether statements about the data in a scatter plot are true. Stimulus Guidelines: Context should be familiar to students 13–15 years old. Scatter plot will have an informative title...
Stimulus
The student is presented with a situation that involves a relationship between two quantities and a scatter plot of measurements of those quantities with sufficient points to demonstrate a linear or nonlinear relationship.
Example 1
Example Stem: This scatter plot shows the relationship between the average weight and average heart rate for 11 different animals.
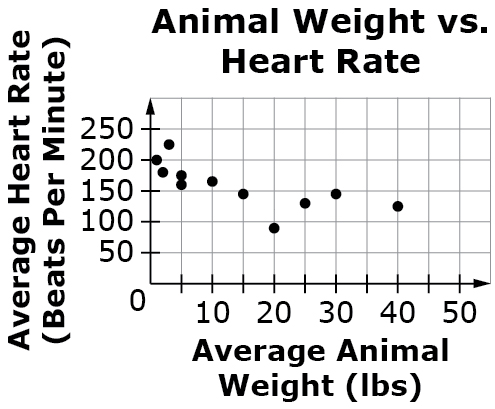
Select True or False for each statement based on the scatter plot.
| Statement | True | False |
|---|---|---|
| There is a positive association between average weight and average heart rate for animals. | ||
| Animals with higher body weights tend to have lower heart rates than animals with lower body weights. | ||
| For animals weighing 20 lbs or less, there is a linear association between average weight and average heart rate. |
Rubric: (1 point) Student determines each statement as being either true or false (e.g., F, T, T) Each statement that interprets the scatter plot and may involve clustering in reference to the line of best fit, positive or negative associations, linear associations, nonlinear associations, or the effect of outliers.

