Grade 8 - Claim 1 - Target G
 Back to Results
Back to ResultsMathematics
Target G
Understand congruence and similarity using physical models, transparencies, or geometry software
Sample Item
Grade 8Test
Claim 1
Concepts and Procedures
Standards
G-1
Verify experimentally the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations.
G-1a
Lines are taken to lines, and line segments to line segments of the same length.
G-1b
Angles are taken to angles of the same measure.
G-1c
Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines.
G-2
Understand that a two-dimensional figure is congruent to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, and translations; given two congruent figures, describe a...
G-3
Describe the effect of dilations, translations, rotations, and reflections on two-dimensional figures using coordinates.
G-4
Understand that a two-dimensional figure is similar to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, translations, and dilations; given two similar two-dimensional figures,...
G-5
Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angle of triangles, about the angles created when parallel lines are cut by a transversal, and the angle-angle criterion for...
Clarifications
Technology enhanced items will be used to allow students to “draw” lines, line segments, angles, and parallel lines after undergoing rotations, reflections, and translations. Similar technology enhanced items will ask students to produce a...
Range Achievement Level Descriptors
Evidence Required
1
The student verifies that rigid transformations preserve distance and angle measures.
2
The student describes sequences of rotations, reflections, translations, and dilations that can verify whether two-dimensional figures are similar or congruent to each other.
3
The student constructs a new figure after the original figure is dilated, rotated, reflected, or translated.
4
The student describes the effect of dilations, translations, rotations, and reflections on two-dimensional figures using coordinates.
Item Guidelines

Depth of Knowledge
M-DOK1
Recall includes the recall of information such as fact, definition, term, or a simple procedure, as well as performing a simple algorithm or applying a formula. That is, in mathematics a one-step, well-defined, and straight algorithmic procedure should be...
M-DOK2
Skill/Concept includes the engagement of some mental processing beyond a habitual response. A Level 2 assessment item requires students to make some decisions as to how to approach the problem or activity, whereas Level 1 requires students to demonstrate a...
Allowable Item Types
- Equation/Numeric
- Matching Tables
- Graphing
- Hot Spot
Allowable Stimulus Materials
two-dimensional geometric figures, the coordinate plane, two-dimensional geometric figures in the coordinate plane
Key/Construct Relevant Vocabulary
angle, transformation, translation, translate, rotation, rotate, reflection, reflect, dilation, dilate, line segment, similar, congruent, parallel, transversal, exterior angle, interior angle, angle-angle criterion, scale factor, vertical angles, adjacent angle, supplementary angles, complementary angles
Allowable Tools
Calculator
Target-Specific Attributes
Rotations are only multiples of 90 degrees about the origin. Reflections are only over the x- and y-axes. Dilations are only with the origin as the center. There are at most three transformations in a sequence of...
Accessibility
Item writers should consider the following Language and Visual Element/Design guidelines [1] when developing items. Language Key Considerations: Use simple, clear, and easy-to-understand language needed to assess the construct or aid in the understanding of the...
Development Notes
Much of the evidence for 8.G.A will be assessed in Claim 3.


Task Models
Task Model 1a

Item Types
Equation/NumericDepth of Knowledge
M-DOK1Standards
G-1
Target Evidence Statement
The student verifies that rigid transformations preserve distance and angle measures.
Allowable Tools
Calculator
Task Description
Prompt Features: The student is prompted to give a length or angle measure in a geometric figure after one rigid transformation. Stimulus Guidelines: The distance formula should not be needed to find the length of the...
Stimulus
The student is presented with an image or description of a geometric object and one rigid transformation.
Example 1
Example Stem 1: Line segment DE is translated left 3 units and down 2 units to form line segment D’E’.
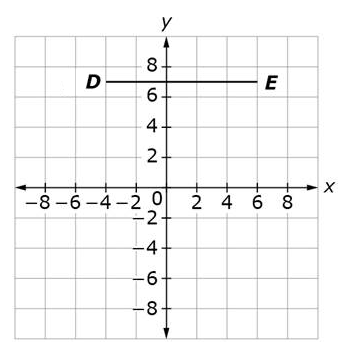
Enter the distance, in units, between point D’ and point E’.
Rubric: (1 point) The student gives the correct measure (e.g., 10).
Example 2
Example Stem 2: Line segment FG begins at (–2, 4) and ends at (–2, –3). The segment is translated left 3 units and up 2 units to form line segment F′G′.
Enter the length, in units, of line segment F′G′.
Rubric: (1 point) The student gives the correct measure (e.g., 7).

