Grade 3 - Claim 1 - Target I
 Back to Results
Back to ResultsClaim 1
Concepts and Procedures
Standards
MD-5
Recognize area as an attribute of plane figures and understand concepts of area measurement.
MD-5a
A square with side length 1 unit, called "a unit square," is said to have "one square unit" of area, and can be used to measure area.
MD-5b
A plane figure which can be covered without gaps or overlaps by n unit squares is said to have an area of n square units.
MD-6
Measure areas by counting unit squares (square cm, square m, square in, square ft, and improvised units).
MD-7
Relate area to the operations of multiplication and addition.
MD-7a
Find the area of a rectangle with whole-number side lengths by tiling it, and show that the area is the same as would be found by multiplying the side lengths.
MD-7b
Multiply side lengths to find areas of rectangles with whole-number side lengths in the context of solving real world and mathematical problems, and represent whole-number products as rectangular areas in mathematical reasoning....
MD-7c
Use tiling to show in a concrete case that the area of a rectangle with whole-number side lengths a and b + c is the sum of a × b and a × c. Use area models to represent the distributive property in mathematical reasoning....
MD-7d
Recognize area as additive. Find areas of rectilinear figures by decomposing them into non-overlapping rectangles and adding the areas of the non-overlapping parts, applying this technique to solve real world problems.
Clarifications
Some tasks associated with this target should assess conceptual understanding of area as a measurable attribute of plane figures. All figures in such problems should be rectilinear and coverable without gaps or overlaps by...
Range Achievement Level Descriptors
Evidence Required
1
The student measures areas by counting unit squares.
2
The student finds areas of rectilinear figures by decomposing them into non-overlapping rectangles and adding the areas of the non-overlapping parts.
3
The student finds the area of a rectangle with whole-number side lengths by tiling it, and shows that the area is the same as would be found by multiplying the side lengths....
Item Guidelines

Depth of Knowledge
M-DOK2
Skill/Concept includes the engagement of some mental processing beyond a habitual response. A Level 2 assessment item requires students to make some decisions as to how to approach the problem or activity, whereas Level 1 requires students to demonstrate a...
Allowable Item Types
- Equation/Numeric
- Multiple Choice, single correct response
Allowable Stimulus Materials
None
Key/Construct Relevant Vocabulary
unit square, area, square unit, plane figure, square centimeter, square meter, square inch, square feet
Allowable Tools
None
Target-Specific Attributes
All figures in such problems should be rectilinear and coverable without gaps or overlaps by unit squares.
Accessibility
Item writers should consider the following Language and Visual Element/Design guidelines [1] when developing items. Language Key Considerations: Use simple, clear, and easy-to-understand language needed to assess the construct or aid in the understanding of the...
Development Notes
Some of the expectations in 3.MD.C.7 (such as using tiling to show that area of a rectangle with whole number side lengths is the same as would be found by multiplying the side lengths)...


Task Models
Task Model 1

Item Types
Equation/NumericDepth of Knowledge
M-DOK2Standards
MD-6
Target Evidence Statement
The student measures areas by counting unit squares.
Allowable Tools
None
Task Description
Prompt Features: The student is prompted to find the area of a figure by counting whole and/or half unit squares. Stimulus Guidelines: Item difficulty can be adjusted via these example methods: Student counts whole unit squares on...
Stimulus
The student is presented with a shaded figure in a grid and determines the total area, in square units, of the figure.
Example 1
Example Stem 1: Use this diagram to solve the problem.
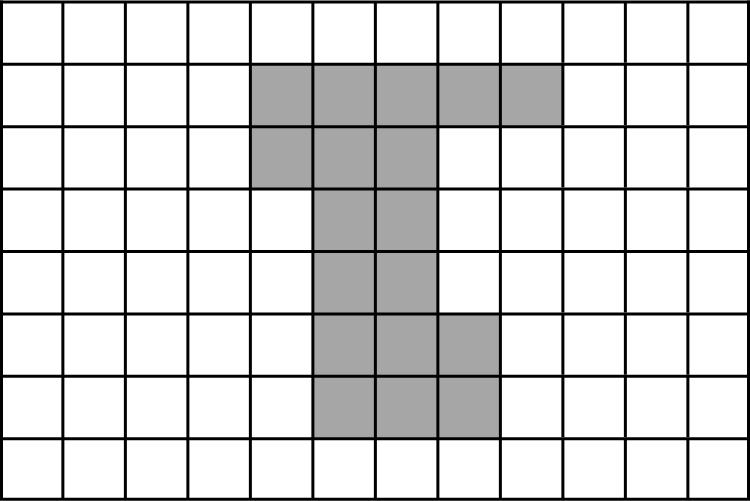
Enter the area, in square units, of the shaded figure in the response box.
Rubric: (1 point) The student correctly enters the area, in square units, of the shaded figure (e.g., 18).
Example 2
Example Stem 2: Use this diagram to solve the problem.
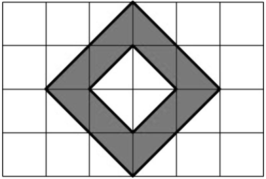

Enter the area, in square units, of the shaded figure in the response box.
Rubric: (1 point) The student correctly enters the area, in square units, of the shaded figure (e.g., 6).

