Grade 3 - Claim 1 - Target F
 Back to Results
Back to ResultsClaim 1
Concepts and Procedures
Standards
NF-1
Understand a fraction 1/b as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned into b equal parts; understand a fraction a/b as the quantity formed by a parts of size 1/b.
NF-2
Understand a fraction as a number on the number line; represent fractions on a number line diagram.
NF-2a
Represent a fraction 1/b on a number line diagram by defining the interval from 0 to 1 as the whole and partitioning it into b equal parts. Recognize that each part has size 1/b and that...
NF-2b
Represent a fraction a/b on a number line diagram by marking off a lengths 1/b from 0. Recognize that the resulting interval has size a/b and that its endpoint locates the number a/b on the number line.
NF-3
Explain equivalence of fractions in special cases, and compare fractions by reasoning about their size.
NF-3a
Understand two fractions as equivalent (equal) if they are the same size, or the same point on a number line.
NF-3b
Recognize and generate simple equivalent fractions, e.g., 1/2 = 2/4, 4/6 = 2/3. Explain why the fractions are equivalent, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.
NF-3c
Express whole numbers as fractions, and recognize fractions that are equivalent to whole numbers. Examples: Express 3 in the form 3 = 3/1; recognize that 6/1 = 6; locate 4/4 and 1 at...
NF-3d
Compare two fractions with the same numerator or the same denominator by reasoning about their size. Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the two fractions refer to the same whole. Record...
Clarifications
Some of these tasks should assess conceptual understanding of unit fractions and other fractions as detailed in 3.NF.A.1 and 3.NF.A.2 [1]. Other tasks for this cluster should involve equivalence of fractions as detailed in...
Range Achievement Level Descriptors
Evidence Required
1
The student identifies a fraction 1/b as 1 part of a whole that is partitioned into b equal parts, and a fraction a/b as the quantity formed by a parts of size...
2
The student identifies and represents fractions on a number line using the interval 0-1 as the whole with or without partitioning.
3
The student identifies two fractions as equal if they are the same size or the same point on a number line.
4
The student generates simple equal fractions using a visual fraction model.
5
The student expresses whole numbers as fractions and recognizes fractions equal to whole numbers.
6
The student compares two fractions with the same numerator or the same denominator using the symbols
<, = ,>.
Item Guidelines

Depth of Knowledge
M-DOK1
Recall includes the recall of information such as fact, definition, term, or a simple procedure, as well as performing a simple algorithm or applying a formula. That is, in mathematics a one-step, well-defined, and straight algorithmic procedure should be...
M-DOK2
Skill/Concept includes the engagement of some mental processing beyond a habitual response. A Level 2 assessment item requires students to make some decisions as to how to approach the problem or activity, whereas Level 1 requires students to demonstrate a...
Allowable Item Types
- Multiple Choice, single correct response
- Equation/Numeric
- Graphing
- Drag and Drop
- Multi-Select, multiple correct response
- Hot Spot
- Matching Tables
Allowable Stimulus Materials
visual fraction models, number lines, equations, area models, strip diagram models
Key/Construct Relevant Vocabulary
equal, denominator, numerator, less than, greater than, number line
Allowable Tools
None
Target-Specific Attributes
Fractions in 3rd grade are limited to denominators of 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8. In fraction comparisons, all fractions must have the same numerator or denominator. Unit fractions are 1 part of the...
Accessibility
Item writers should consider the following Language and Visual Element/Design guidelines [1] when developing items. Language Key Considerations: Use simple, clear, and easy-to-understand language needed to assess the construct or aid in the understanding of the...
Development Notes
None


Task Models
Task Model 1

Item Types
Multiple Choice, single correct responseDepth of Knowledge
M-DOK1Standards
NF-1
Target Evidence Statement
The student identifies a fraction 1/b as 1 part of a whole that is partitioned into b equal parts, and a fraction a/b as the quantity formed by a parts of size 1/b using a model. For this evidence statement,...
Allowable Tools
None
Task Description
Prompt Features: The student is prompted to select the fraction represented by the model or the model represented by the fraction. Stimulus Guidelines: Denominators are limited to 2, 3, 4, 6 and 8. Area models are polygons...
Stimulus
The student is presented with a fraction in the form of .
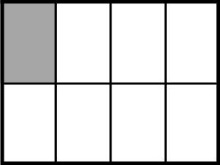
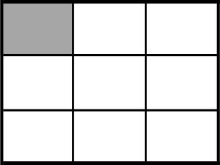
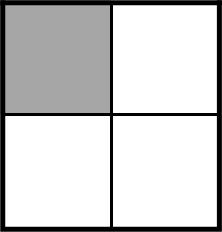
Example 1
Example Stem 1: Which model shows of the whole figure shaded?
A.
B.
C.
D.
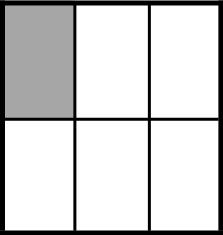
Rubric: (1 point) The student selects the correct model (e.g., A).
Example 2
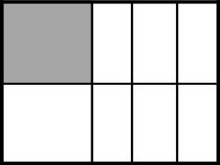
Example Stem 2: Which model shows of the whole figure shaded?
A.
B.
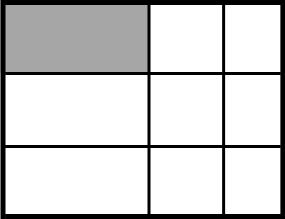
C.

D.

Rubric: (1 point) The student selects the correct model (e.g., C).
Example 3
Example Stem 3: Which model shows of the whole figure shaded?
A.
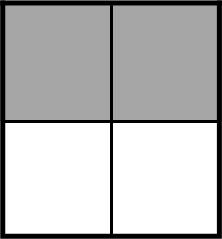
B.

C.
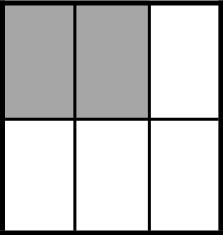
D.
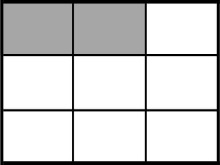
Rubric: (1 point) The student selects the correct model (e.g., C).
Example 4
Example Stem 4: Which model shows of the whole figure shaded?
A.

B.

C.
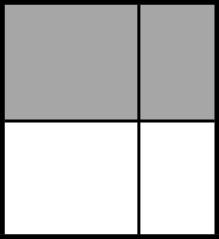
D.
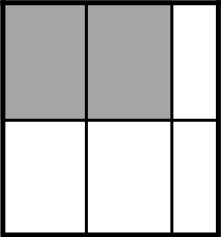
Rubric: (1 point) The student selects the correct model (e.g., B).

