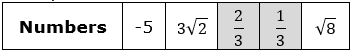Grade 11 - Claim 1 - Target B
 Back to Results
Back to ResultsClaim 1
Concepts and Procedures
Standards
RN-3
Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of a rational number and an irrational number is irrational; and that the product of a nonzero...
Clarifications
Tasks for this target will require students to demonstrate understanding of operations with rational and irrational numbers. Tasks that ask students to explain why operations with rational and irrational numbers lead to either rational...
Range Achievement Level Descriptors
Evidence Required
1
The student provides examples of addition or multiplication problems that will have sums or products of a specified type (rational or irrational).
2
The student determines whether the sum of two numbers is a rational number or an irrational number.
3
The student determines whether the product of two numbers is a rational number or an irrational number.
4
The student provides an abstract generalization that the sum or product of any two rational numbers is rational, the sum of a rational number and an irrational number is irrational,...
Item Guidelines

Depth of Knowledge
M-DOK1
Recall includes the recall of information such as fact, definition, term, or a simple procedure, as well as performing a simple algorithm or applying a formula. That is, in mathematics a one-step, well-defined, and straight algorithmic procedure should be...
M-DOK2
Skill/Concept includes the engagement of some mental processing beyond a habitual response. A Level 2 assessment item requires students to make some decisions as to how to approach the problem or activity, whereas Level 1 requires students to demonstrate a...
Allowable Item Types
- Hot Spot
- Matching Tables
- Multi-Select, multiple correct response
Allowable Stimulus Materials
products or sums of rational and irrational numbers, number type (rational or irrational)
Key/Construct Relevant Vocabulary
rational number, irrational number, real number
Allowable Tools
None
Target-Specific Attributes
Only sums and products of two numbers are used.
Accessibility
Item writers should consider the following Language and Visual Element/Design guidelines [1] when developing items. Language Key Considerations: Use simple, clear, and easy-to-understand language needed to assess the construct or aid in the understanding of the...
Development Notes
None


Task Models
Task Model 1

Item Types
Hot SpotDepth of Knowledge
M-DOK2Standards
RN-3
Target Evidence Statement
The student provides examples of addition or multiplication problems that will have sums or products of a specified type (rational or irrational).
Allowable Tools
None
Task Description
Prompt Features: The student gives an example of either an addition or multiplication problem with either a rational or irrational product or sum. Stimulus Guidelines: Four or more numbers are given, of which two are rational numbers...
Stimulus
The student is presented with rational and irrational numbers.
Example 1
Example Stem 1: Select two numbers whose sum, when added, would be irrational.
| Numbers | -5 | 3 |
|---|
Rubric:
(1 point) The student selects two numbers that satisfy the given conditions. Multiple correct responses are possible and will all need to be included in the scoring rubric. Only example responses are shown below.
Example Stem 1:

Example 2
Example Stem 2: Select two numbers whose sum, when added, would be rational.
| Numbers | -5 | 3 |
|---|
Rubric:
(1 point) The student selects two numbers that satisfy the given conditions. Multiple correct responses are possible and will all need to be included in the scoring rubric. Only example responses are shown below.
Example Stem 2:

Example 3
Example Stem 3: Select two numbers whose product, when multiplied, would be irrational.
| Numbers | -5 | 3 |
|---|
Rubric:
(1 point) The student selects two numbers that satisfy the given conditions. Multiple correct responses are possible and will all need to be included in the scoring rubric. Only example responses are shown below.
Example Stem 3:

Example 4
Example Stem 4: Select two numbers whose product, when multiplied, would be rational.
| Numbers | -5 | 3 |
|---|
Rubric:
(1 point) The student selects two numbers that satisfy the given conditions. Multiple correct responses are possible and will all need to be included in the scoring rubric. Only example responses are shown below.
Example Stem 4: